The Economics of Caffeine
Welcome to this edition of Deja Brew, where we dive deep into the fascinating world of caffeine (yes, we know. FINALLY) —not just as a daily ritual, but as a powerful economic force.
From the first sip that kickstarts your morning to the growing industry that fuels millions worldwide, caffeine’s influence is far-reaching.
In this issue, we explore the economic implications of our caffeine consumption, examining the delicate balance between the health costs and the undeniable productivity boost it provides. We’ll delve into a compelling study that sheds light on how caffeine impacts workplace efficiency, unpack the challenges India faces in transitioning to greener production methods, and discuss the evolving trends in caffeine consumption across the country.
India's love affair with caffeine is deeply rooted in its rich tradition of coffee and tea production. From the lush tea gardens of Assam and Darjeeling to the coffee estates of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, India is one of the few countries that produces both beverages in abundance. Millions of Indians (deja) brew either of the two daily, driving a significant portion of the country’s agricultural economy. Behind each cup lies a fascinating journey, shaped by India's diverse climates, skilled farmers, and intricate supply chains that connect rural plantations to urban cafes.
Unlike tea, coffee is predominantly an export-oriented commodity as more than 70% of the coffee produced is exported. Despite this India remains a minor player in the international coffee market. International prices very heavily influence Indian coffee production. On the contrary, India is known as a ‘tea powerhouse’ and is fighting among other heavyweights like Kenya and China to establish its dominance.
ECONOMIC IMPACT OF CAFFEINE ON PRODUCTIVITY: Is It Worth the Buzz?
From tech hubs to financial districts, the consumption of caffeine is deeply embedded in workplace culture, where it is not just a drink but also a crucial aid in maintaining focus, reducing fatigue, and enhancing cognitive functions.
The economic benefits of coffee and tea consumption in the workplace are well-documented. Studies consistently show that moderate caffeine intake can improve cognitive functions like memory, attention, and overall mental performance.
For industries that rely heavily on intellectual work and rapid decision-making, such as technology and finance, these benefits are not just theoretical but translate into substantial economic gains.
In the technology sector, for instance, where innovation and problem-solving are key, coffee is often viewed as a fuel for creativity and sustained concentration. Companies like Google and Apple are known for providing high-quality coffee in their offices, recognizing that a well-caffeinated workforce is more productive. A study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology highlighted that caffeine’s cognitive-enhancing effects could lead to billions of dollars in additional output annually, making the investment in coffee well worth it.
The financial sector also sees significant benefits from caffeine consumption. In this high-pressure environment, where decisions can have immediate and substantial financial implications, even a slight boost in productivity can result in considerable financial gains.
During critical periods such as market openings, earnings reports, or economic announcements, the ability to stay alert and focused is paramount. Here, the cost of a cup of coffee is negligible compared to the potential return on investment that comes from enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Despite these benefits, the costs associated with daily coffee and tea consumption are not insignificant.
However, when these costs are compared to productivity gains—such as improved focus, quicker problem-solving, and reduced absenteeism—the expenditure often justifies itself. Many companies recognize this and provide free or subsidized coffee and tea as part of their employee benefits, seeing it as a direct investment in productivity.
A Study on the Benefits of Caffeine in the Workplace
Setting: In the first study 110 volunteers, all of whom were regular caffeine consumers, rated their alertness and carried out a simple reaction time task before and after work on a Monday and Friday. Caffeine consumption during the day was recorded and volunteers were subdivided into low and high consumers based on a median split (220 mg/day).
In the first analyses associations between caffeine consumption and frequency of cognitive failures were examined in a sample of 1253 white-collar workers. The second set of analyses examined associations between caffeine consumption and accidents at work in a sample of 1555 workers who were especially at risk of having an accident.
Result: In the first study, people who drank more caffeine felt much more alert throughout the day and had faster reaction times. The second study found that those who consumed more caffeine experienced fewer cognitive slips and workplace accidents. After accounting for other factors, higher caffeine intake was linked to roughly half the risk of frequent cognitive failures and accidents at work.
Source: Smith, Andrew P. “Caffeine at work.” Human psychopharmacology vol. 20,6 (2005): 441-5. doi:10.1002/hup.705
The Health and Wellness Aspect
Caffeine consumption is deeply embedded in our daily lives, whether through the chai break we all need in the middle of work that fuels conversations, or the filter coffee that drives productivity. However, while caffeine offers undeniable economic benefits (I write this as I sip on my coffee), particularly in terms of increased alertness and productivity, it also has associated healthcare costs. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis specific to India provides insights into the trade-offs between these benefits and the potential health risks of excessive consumption.
In a country where long working hours and high levels of competition are the norm, caffeine plays a crucial role in maintaining productivity. Tea and coffee are not just beverages but essential tools for professionals, students, and labourers who rely on them to stay alert and focused. The economic impact of this increased productivity can be substantial. For instance:
- Workplace Productivity: We all know that a well-timed cup of tea or coffee can enhance concentration and efficiency, particularly in high-pressure environments like IT firms, BPOs, and academic institutions. This boost in productivity directly contributes to the economic output of individuals and, by extension, the sectors they work in.
- Cultural and Social Contributions: In India, tapris (roadside tea stalls - for the uninitiated) are cultural hubs where business deals are struck, and ideas are exchanged. These venues contribute to the economy not only through direct sales but also by fostering an environment conducive to economic activity.
But What About The Price of Excessive Consumption?
While moderate caffeine consumption can be beneficial, excessive use leads to a range of health issues, including insomnia, anxiety, digestive problems, and heart palpitations. In India, where access to healthcare is variable and insurance coverage is not universal, the healthcare costs associated with caffeine-related health issues can be significant.
- Insurance Premiums: As the prevalence of caffeine-related health issues rises, there could be a corresponding increase in insurance premiums. For individuals, this means higher out-of-pocket expenses, and for employers who provide health insurance, it could result in increased costs for group health plans.
- Healthcare System Burden: The public healthcare system in India is already under pressure, and caffeine-related health issues could add to this burden. The treatment of conditions exacerbated by excessive caffeine consumption, such as hypertension and anxiety disorders, can lead to increased demand for healthcare services, straining the system further.
Balancing the Scales: Moderation is Key
The key to maximising the benefits of caffeine while minimising the costs lies in moderation. Public awareness campaigns and workplace wellness programs that promote balanced caffeine consumption could help reduce the incidence of related health issues, thereby lowering healthcare costs. At the same time, these initiatives could ensure that the economic benefits of increased productivity and alertness are fully realised.
By conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis, India can better understand the economic trade-offs of caffeine consumption. This understanding can inform public health policies, workplace guidelines, and even insurance practices, ensuring that the benefits of caffeine are enjoyed without disproportionately high costs.
The Shifting Trends in Current Times
Younger consumers' rising interest in energy drinks and caffeine alternatives is indicative of a change in their perspective on wellness and vitality. Younger consumers—Gen Z and millennials in particular—are gravitating toward natural caffeine substitutes and energy drinks as alternatives to regular coffee because they fit in with their busy lifestyles and ideals.
Energy Drinks: A Popular Choice
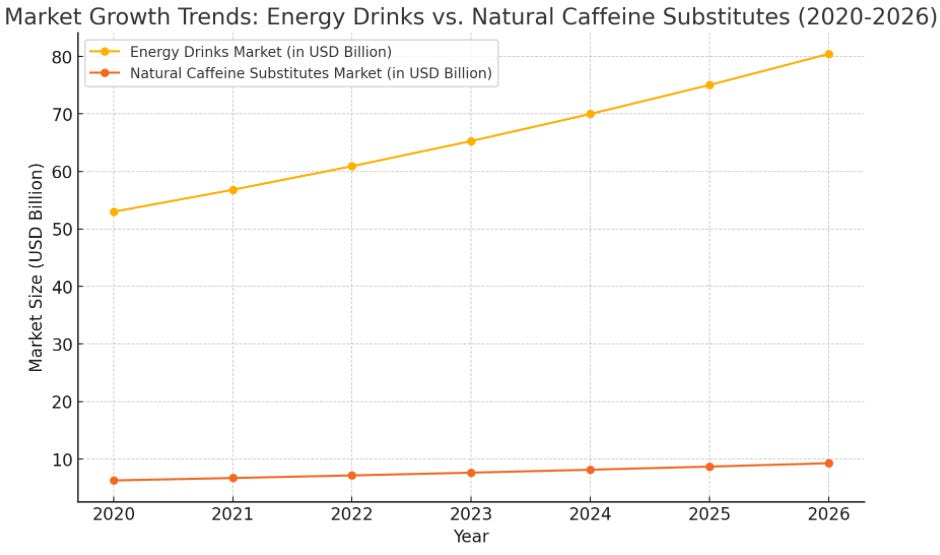
Younger customers who frequently balance hectic schedules, employment, school, and social activities have made energy drinks a mainstay in their diets. The global market for energy drinks was estimated to be worth USD 53 billion in 2020 and is projected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% to reach roughly USD 86 billion by 2026, according to a report by Allied Market Research. Younger consumers, who are lured to these drinks' instant energy boost, variety of flavors, and useful additives like taurine and B vitamins, are mostly responsible for this growth.
The Shift Towards Natural Caffeine Substitutes
At the same time, there's a noticeable shift toward natural caffeine substitutes among health-conscious younger consumers. Natural caffeine-containing products like yerba mate, matcha, and guayusa are becoming more and more popular because they are thought to provide a more balanced and long-lasting energy boost than the synthetic caffeine found in conventional energy drinks.
Younger consumers are shaking up the beverage scene, ditching old habits in favor of energy drinks and caffeine substitutes that offer more than just a quick jolt. With a strong focus on convenience, health, and sustainability, they’re driving a surge in demand for products that fit their active, wellness-driven lifestyles. As they continue to prioritize clean energy and functional benefits, the market for both classic energy drinks and natural alternatives is set to explode. Brands that tap into this wave with innovative, health-focused offerings are poised to lead the charge in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Economics of Decaf and Alternatives
In today's fast-paced world, there is a strong coffee culture, more and more people are looking for alternatives that match healthier lifestyles. The market for decaffeinated goods and herbal and chicory root teas—two caffeine substitutes—is growing quickly. The need for decisions that prioritise well-being, and more knowledge of the negative health effects of caffeine is what is driving this trend.
The price of decaffeinated products and caffeine substitutes vary significantly depending on the type of, brand, and processing method. The Swiss Water Process, a popular chemical-free method of decaffeination, is particularly costly because it requires more time and resources, which are reflected in the final price of the product. On average, consumers can expect to pay 10-20% more for decaffeinated coffee compared to its caffeinated counterpart. Similarly, chicory root and herbal teas, as alternatives to coffee, often come at a premium, especially when they are organic, non-GMO, or blended with other high-quality ingredients. Chicory-based coffee substitutes can range in price from $10 to $20 per pound, depending on the brand and the blend. Herbal teas, particularly those with added functional benefits like adaptogens, usually command higher prices.
Why are consumers opting for caffeine alternatives?
Health and wellness concerns are a major factor in why people are switching to caffeine substitutes. Due to the negative effects of caffeine on anxiety, jitters, and sleep, many people look for decaffeinated items that still provide the comforting ritual of a morning cup of coffee without the negative effects. This shift is particularly noticeable among millennials and Gen Z consumers, who are more likely to prioritise their mental and physical well-being. Furthermore, because caffeine can aggravate acid reflux and irritate the stomach lining, people are looking into alternatives like chicory root, which tastes similar to coffee and also functions as a prebiotic to enhance gut health.
Looking ahead, the market for decaffeinated products and caffeine substitutes is expected to grow significantly. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global decaffeinated coffee market was valued at approximately USD 1.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely attributed to the rising prevalence of health-conscious consumers who seek the flavour of coffee without the negative effects of caffeine.
Companies are responding to this demand by innovating with unique blends and flavors, such as combining chicory with superfoods like turmeric or ashwagandha, which appeal to consumers seeking both taste and health benefits. The herbal tea market, for instance, was valued at USD 3.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 4.7% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for natural and organic products, as well as the growing popularity of functional beverages that offer health benefits beyond basic hydration.
As more people focus on their health and well-being, the demand for decaffeinated products and caffeine alternatives is likely to grow, especially when you consider that a single cup of espresso, has an estimated 60-80 mg of caffeine. With innovative offerings, sustainable practices, and a focus on wellness, the caffeine alternative markets is set for considerable expansion. Whether you're a coffee lover looking to cut back on caffeine or a wellness enthusiast exploring new beverages, now is the perfect time to dive into the world of decaf and caffeine alternatives.
CAFFEINE CONSUMPTION PATTERNS
Caffeine is more than just a morning ritual—it's a global phenomenon with fascinating variations across different income groups and regions.
Socio-Economic Factors:
For those in higher income brackets, caffeine is often a luxury. The availability of premium options and a culture that celebrates sophisticated coffee experiences shape their consumption patterns. According to a 2022 report by the National Coffee Association, high-income consumers are more likely to purchase specialty coffee and spend more on artisanal coffee experiences. This segment is also more likely to frequent upscale coffee shops and cafes.
In contrast, middle-income individuals approach caffeine with a mix of practicality and preference. They typically enjoy coffee from well-known chains or brew it at home, balancing quality with affordability. Their choices are influenced by the need for a reliable caffeine source that fits within their budget while still offering a satisfying experience. Middle-income consumers, hence, balance quality with cost. Data from a 2023 survey by Euromonitor International shows that this group frequently purchases coffee from well-known chains and brews coffee at home, reflecting a preference for both convenience and value.
Lower-income individuals often rely on more economical caffeine options, such as instant coffee or budget-friendly tea. For them, caffeine is not just a daily ritual but a means to manage demanding schedules and long work hours. Their consumption is driven by cost-effectiveness, focusing on getting a caffeine fix without overspending.
Regional differences further highlight how caffeine consumption is shaped by local cultures and lifestyles. In India, caffeine consumption is shaped by both tradition and modern economic trends.
Tea remains a staple across the country, enjoyed daily and widely affordable, making it accessible to all income groups. The Tea Board of India reported that tea consumption was around 850,000 metric tons in 2021, indicating its widespread popularity across all income groups.
Coffee, on the other hand, shows a blend of tradition and modernization. South India has a rich coffee culture with traditional filter coffee, reflecting a long-standing practice. In contrast, urban areas are seeing a rise in café culture as incomes increase, with specialty coffee shops becoming popular among the growing middle class. A 2023 report by Deloitte noted a significant increase in the number of specialty coffee shops in cities like Bangalore, Mumbai, and Delhi, driven by the growing middle class and rising disposable incomes.
For lower-income groups, affordability drives the choice, making instant coffee and tea the preferred options. The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) data from 2019 indicates that lower-income households spend a smaller proportion of their budget on coffee, often choosing more cost-effective options. Overall, India’s caffeine habits illustrate a mix of deep-rooted traditions and evolving economic influences, highlighting how cultural practices adapt to changing economic conditions.
Cultural Economics:
Cultural preferences dramatically shape the market for caffeinated beverages, and their impact extends well into the economic realm. Let’s explore how this plays out in different countries.
In Italy, coffee culture is almost a national treasure, with espresso being the star of the show. Italians don’t just drink coffee; they savor it, often in quick, social bursts throughout the day. According to a 2022 report by the International Coffee Organization, Italy is among the top coffee-consuming countries per capita. This deep-seated love for espresso fuels a market where artisanal coffee shops and bars thrive. Economically, this translates into a robust coffee industry that not only drives substantial revenue but also supports a rich tapestry of local businesses and employment in the hospitality sector.
Contrast this with Japan, where tea, particularly green tea, is deeply integrated into the culture. The Japanese Ministry of Agriculture reported that the country consumes about 100,000 metric tons of green tea annually. This preference is reflected in Japan’s market, which favors traditional tea ceremonies and high-quality tea products. The economic impact here is substantial as well, with the tea industry contributing significantly to both domestic consumption and export revenue, showcasing the country’s commitment to preserving and promoting its tea culture.
Meanwhile, in the United States, coffee culture has evolved into a diverse and dynamic landscape. The National Coffee Association highlights that 62% of Americans drink coffee daily, with a strong preference for specialty and premium options. This trend has spurred the growth of a thriving café culture and a booming market valued at approximately $82 billion in 2023. The economic benefits are vast, including job creation, increased investment in coffee-related businesses, and the expansion of global coffee brands.
In India, the tea market remains dominant, with around 850,000 metric tons consumed annually, as reported by the Tea Board of India. Tea’s cultural significance ensures it remains a staple for all income groups, fostering a significant domestic industry. However, urban areas are experiencing a coffee renaissance. Cities like Bangalore and Mumbai are seeing a surge in specialty coffee shops, driven by a burgeoning middle class. A Deloitte 2023 report notes this shift, illustrating how changing tastes and rising incomes are fueling new economic opportunities in the coffee sector.
Whether through the beloved espresso in Italy, the ceremonial green tea in Japan, the diverse coffee culture in the U.S., or the evolving coffee scene in India, these preferences create vibrant markets and drive significant economic activity.
Greener Coffee and Tea Production in India
India faces significant challenges in ensuring that the production of these beverages is environmentally sustainable. The traditional methods of growing and processing coffee and tea have substantial environmental costs, including deforestation, soil degradation, and excessive water use.
For instance, producing a kilogram of tea can require up to 20,000 liters of water, which is a significant concern in water-scarce regions. Similarly, coffee farming in areas like Karnataka and Tamil Nadu often leads to soil erosion and the overuse of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, which can have long-lasting negative impacts on the environment.
However, there is a growing movement toward sustainable coffee and tea production in India. Practices such as organic farming, which avoids the use of synthetic chemicals, are slowly becoming more widespread.
Additionally, fair trade initiatives that ensure better wages and working conditions for farmers are gaining popularity. The market for organic and fair trade tea and coffee in India is growing, reflecting increased consumer awareness and a willingness to pay a premium for sustainably produced products.
These sustainable practices, while initially more expensive, offer long-term economic and environmental benefits.
By reducing the ecological footprint of coffee and tea production and improving the livelihoods of farmers, these practices help ensure the long-term viability of the industry in India. They also align with the global trend toward more eco-friendly consumption, which is increasingly important to consumers who are concerned about the environmental impact of their choices.
Final Sip: The Economics of Caffeine in a Cup
From the global supply chain to the workplace coffee machine, caffeine is more than just a stimulant—it’s a critical component of the global economy. Whether it’s coffee, tea, energy drinks, or supplements, every sip is part of a larger economic story that touches on productivity, health, culture, and sustainability.
India's deep-rooted coffee and tea culture fuels both its economy and daily life, but with that comes a complex balance of benefits and challenges. From the clear productivity gains in high-stakes industries to the rising health costs associated with excessive consumption, caffeine's impact is both profound and varied. As the market adapts to new demands for greener production methods and healthier alternatives, particularly in a rapidly changing country like India, the future of caffeine is set to evolve in intriguing ways. Whether through decaffeinated options, sustainable practices, or innovative new products, the landscape is shifting, reflecting a broader awareness of the trade-offs involved in our caffeine choices.
As you sip your next cup, consider not just the immediate boost it gives you, but the larger implications brewing beneath the surface.
In case you missed out on the last edition of Deja Brew:
Demographic Time Bomb: A Hidden Threat to our Economy
We human beings are pretty incredible. From the invention of fire to being pretty close to having a sun of our own (nuclear fusion), we have been making breakthroughs after breakthroughs, and all of this piles up and increases the pace of progress.